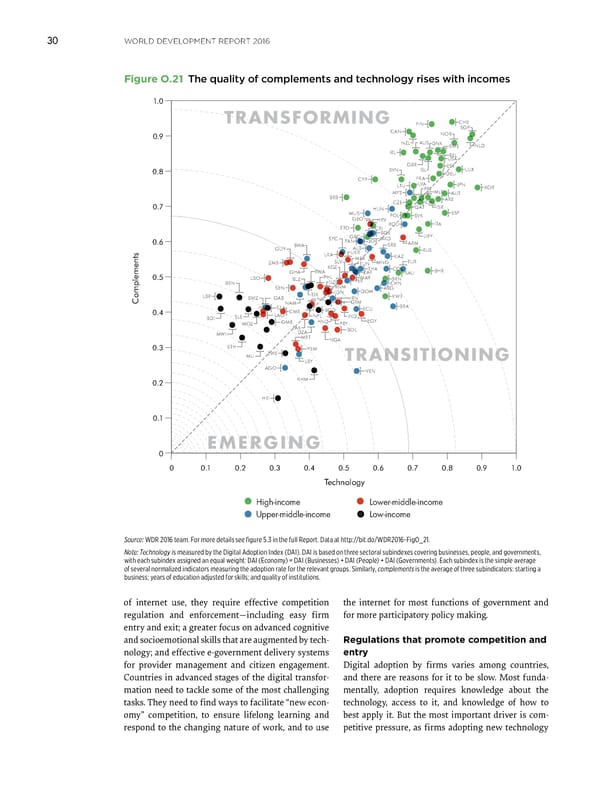
WORLD DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2016 30 Figure O.21 The quality of complements and technology rises with incomes 1.0 TRANSFORMING FIN CHE CAN SGP 0.9 NOR NZL AUS DNK SWE NLD IRL BEL USA GBR EST 0.8 SVN ISL DEU LUX CYP FRA LTU LVA JPN KOR MYS PRT MLT AUT BRB ARE CZE CHL 0.7 HUN QAT ISR MUS POL SVK ESP GEO HRV TTO ROU ITA CRI GRC BGR URY 0.6 SYC PAN JOR MKD BWA SRB ARM GUY ALB RUS LKA UKR KAZ SLV MEX MNG TUR ZMB KGZ TUN GHA RWA THA COL BHR ZAF SAU 0.5 LSO BLZ PHL MAR BRN BEN UZB PER CHN SEN VNM ARG TJK IDN DOM LBR SWZ GAB NIC IRN KWT Complements NAM KEN GTM BRA 0.4 TZA CMR BGD ECU BDI SLE LAO NPL IND MOZ GMB HND PRY EGY PAK BOL MWI DZA MRT NGA 0.3 ETH YEM MLI ZWE TRANSITIONING LBY AGO VEN 0.2 KHM HTI 0.1 EMERGING 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 Technology High-income Lower-middle-income Upper-middle-income Low-income Source: WDR 2016 team. For more details see figure 5.3 in the full Report. Data at http://bit.do/WDR2016-FigO_21. Note: Technology is measured by the Digital Adoption Index (DAI). DAI is based on three sectoral subindexes covering businesses, people, and governments, with each subindex assigned an equal weight: DAI (Economy) = DAI (Businesses) + DAI (People) + DAI (Governments). Each subindex is the simple average of several normalized indicators measuring the adoption rate for the relevant groups. Similarly, complements is the average of three subindicators: starting a business; years of education adjusted for skills; and quality of institutions. of internet use, they require effective competition the internet for most functions of government and regulation and enforcement—including easy firm for more participatory policy making. entry and exit; a greater focus on advanced cognitive and socioemotional skills that are augmented by tech- Regulations that promote competition and nology; and effective e-government delivery systems entry for provider management and citizen engagement. Digital adoption by firms varies among countries, Countries in advanced stages of the digital transfor- and there are reasons for it to be slow. Most funda- mation need to tackle some of the most challenging mentally, adoption requires knowledge about the tasks. They need to find ways to facilitate “new econ- technology, access to it, and knowledge of how to omy” competition, to ensure lifelong learning and best apply it. But the most important driver is com- respond to the changing nature of work, and to use petitive pressure, as firms adopting new technology
 World Development Report 2016 Page 45 Page 47
World Development Report 2016 Page 45 Page 47